Polar Regions
Non-EO
ESA
Quick facts
Overview
| Mission type | Non-EO |
| Agency | ESA |
Polar Regions - Ice Loss Situation in 2021
Antarctic Glacier Named Glasgow to Mark COP26
• October 31, 2021: Nine fast-flowing glaciers in West Antarctica have been named after locations of important climate treaties, conferences and reports. One of the glaciers is now called Glasgow Glacier to mark the city hosting the COP26 climate change conference. All the glaciers are in the Getz region, which, using data from satellites, was found recently to have lost more than 300 gigatons (300 x 109 tons) of ice over the last 25 years. 1) 2)
Glasgow in the UK is currently welcoming more than 100 world leaders to COP26, the 26th UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP26). The conference marks a key moment in human history for our response to climate change.
Nine Newly Named Getz Ice Shelf Glaciers in West Antarctica to Emphasize the World's Climate Crises
• The Geneva Glacier flows at the western end of the Getz Ice Shelf and was named after the world’s first climate conference in 1979.
• The Rio Glacier lies further east and commemorates the first Earth Summit in 1992 where the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change was opened for signatures along with its sisters the Rio convention, the UN convention on biological diversity and the UN convention to combat desertification.
• The Berlin Glacier flows further east and is named after the first Conference of Parties (COP) in 1995, which assessed the progress of dealing with climate change. It marked the uniting of the world to tackle climate change and the agreement on a mandate for future negotiations.
• Still further east lies the Kyoto Glacier commemorating the formal adoption of the Kyoto Protocol at COP3 in 1997, which legally bound developed countries to emission reduction targets.
• The Bali Glacier marks the release of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) forth assessment report in 2007. Around this time, climate science entered into the popular consciousness. At COP13, parties agreed on the Bali road map, which charted the way towards post-2012 outcome with a working group on long-term cooperative action under the convention.
• The Stockholm Glacier honors the IPCC fifth assessment report approval session in 2014. This report represents the biggest ever coming together of scientists at the time.
• The Paris Glacier memorializes the agreement of a legally binding treaty in 2015 that aimed to limit global warming to well below 2°C, preferably below 1.5°C, compared to pre-industrial levels. It was adopted by 196 parties.
• The Incheon Glacier marks the meeting of the IPCC to consider the special report of global warming of 1.5°C in 2015. This marked the first time the three different IPCC working groups worked together to produce a report in an interdisciplinary manner.
• The Glasgow Glacier marks COP26 being held in Glasgow, Scotland, UK in October 2021. The main aims of which are to secure global net zero emissions by the middle of the century, keep the goal 1.5°C within reach, adapt to protect communities and natural habitats, mobilize climate finance, work together to finalize the Paris Rulebook and accelerate action to tackle the climate crisis.
Requested by scientists from the University of Leeds, the new names were approved by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee, and will be added to the British Antarctic Territory Gazetteer for use on all maps, charts and future applications.
Researchers at Leeds’ School of Earth and Environment discovered that between 1994 and 2018, all the glaciers in the Getz region accelerated – on average, by almost 25%, with three glaciers accelerating by over 40%. They revealed that 315 gigatons of ice has been lost from the Getz region over the last 25-years, adding 0.9 mm to global mean sea level; the equivalent of 126 million Olympic swimming pools of water.
The scientists included data from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission and ESA’s CryoSat mission in their research, which will also help determine if these glaciers could collapse in the next few decades and how this would affect future global sea-level rise.
PhD researcher Heather Selley from the University of Leeds requested that the nine unnamed Getz glaciers in her study be named after the locations of major climate treaties, conferences and reports.
Ms Selley said, “We wanted to permanently mark the outstanding effort the scientific community has put into measuring the present-day impact of climate change, and its predicted future evolution. Our study was the first to show that glaciers in this remote region of Antarctica were speeding up.
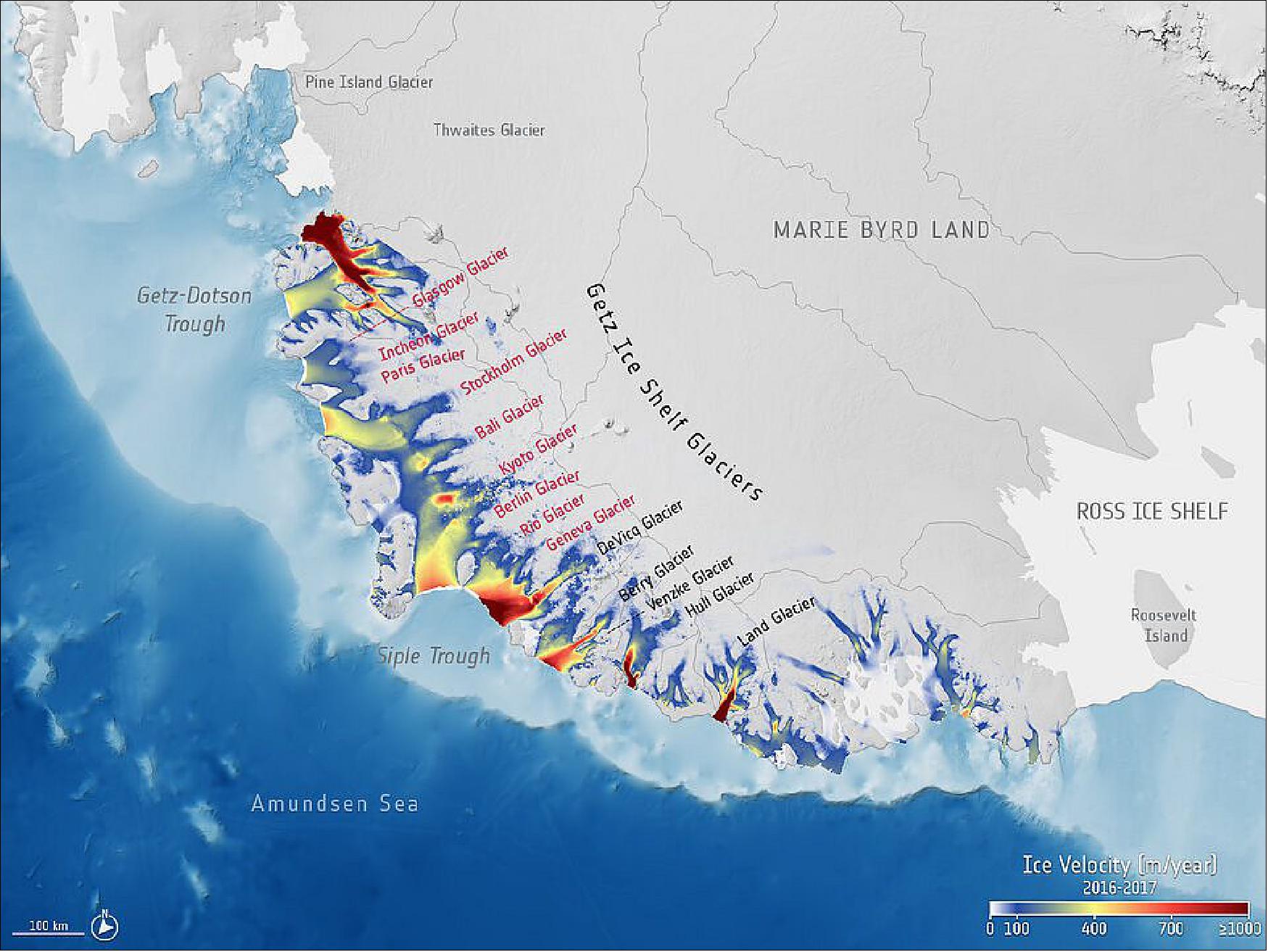
“The glaciers are named in chronological order, with Geneva Glacier marking the first ever climate summit in 1979 on the west of the Getz study region and Glasgow Glacier marking the upcoming COP26 on the east.”

Dramatic changes in Antarctica’s ice have become synonymous with the climate crisis. Over the last 40 years, satellites have observed huge iceberg calving events, change in the flow of glaciers and regions of rapidly thinning ice, all of which improves our understanding of how the ice sheet contribution to sea-level rise has changed and provides essential evidence of the impact of climate change.
Anna Hogg, Associate Professor in Leeds’ School of Earth and Environment, said, “The climate crisis effects all of us, whether through flooding of our homes, increased storm frequency, reduced crop harvests, or the loss of habitats and biodiversity in the natural environment, with some communities impacted much more than others.

“While these new glacier names celebrate the knowledge gained through scientific collaboration and the action taken through policy, it’s clear now that much more must be done. I am inspired by the school climate strikes which remind all of us that we are only temporary gate holders and have a responsibility to protect planet Earth for the next generation. There is no doubt that there is a need for urgent action, we have great hope in the power of international collaboration which can enable significant progress to be made at COP26.”
ESA’s Mark Drinkwater noted, “Indeed, it is fitting that these glaciers in West Antarctica now carry names directly linked to climate research and climate policy-making.
“Satellite observations over the last 30 years or so have been crucial to measuring, understanding and publicizing the dramatic changes taking place in the remote polar regions. ESA’s CryoSat and the EC’s (European Commission) Copernicus Sentinel-1, which ESA developed and operates, are key to the findings about ice loss from Getz. Fortunately, we have other new polar-orbiting monitoring satellites in the pipeline that will ensure global attention remains focused on the climate change impact on these iconic glaciers in the coming decades.”
Change in the Arctic Ice Coverage
References
1) ”Antarctic glacier named Glasgow to mark COP26,” ESA Applications, 31 October 2021, URL: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/
Space_for_our_climate/Antarctic_glacier_named_Glasgow_to_mark_COP26
2) ”‘Glasgow Glacier' named in honour of COP26 Summit,” UK Government Press Release, 31 October 2021, URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/glasgow-glacier-named-in-honour-of-cop26-summit
3) ”Change in the Arctic,” ESA Applications, 02 November 2021, URL: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Videos/2021/09/Change_in_the_Arctic
The information compiled and edited in this article was provided by Herbert J. Kramer from his documentation of: ”Observation of the Earth and Its Environment: Survey of Missions and Sensors” (Springer Verlag) as well as many other sources after the publication of the 4th edition in 2002. - Comments and corrections to this article are always welcome for further updates (eoportal@symbios.space).